Platfio Mobile App Development
By Fangtai Dong
- Published on
- Duration
- 3 Months
- Role
- Front-end Developer
- Purpose
- Profession Year
- Technology
- Vue, JavaScript, Ionic ...
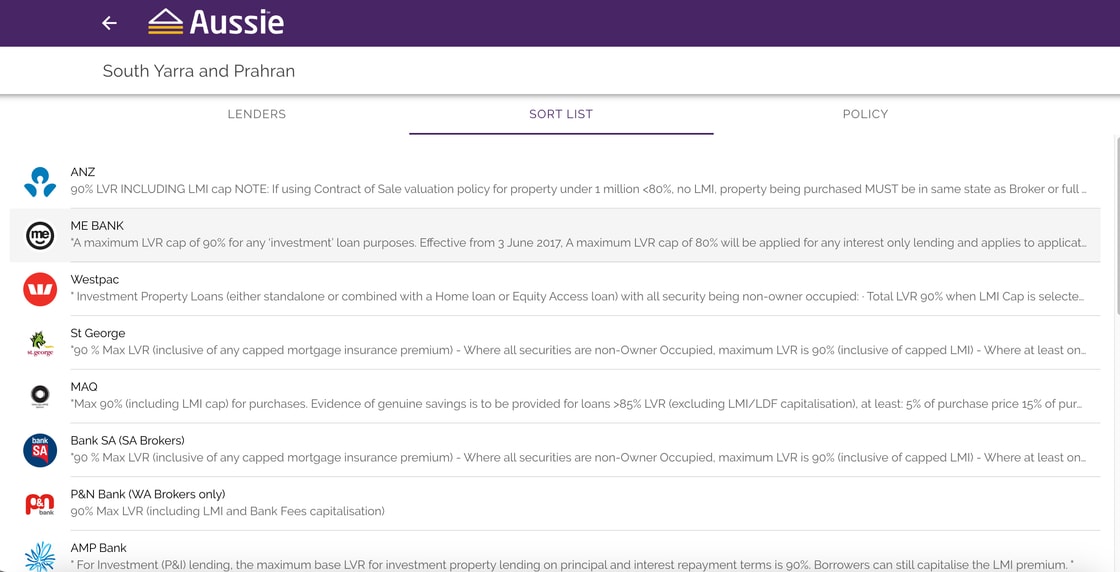
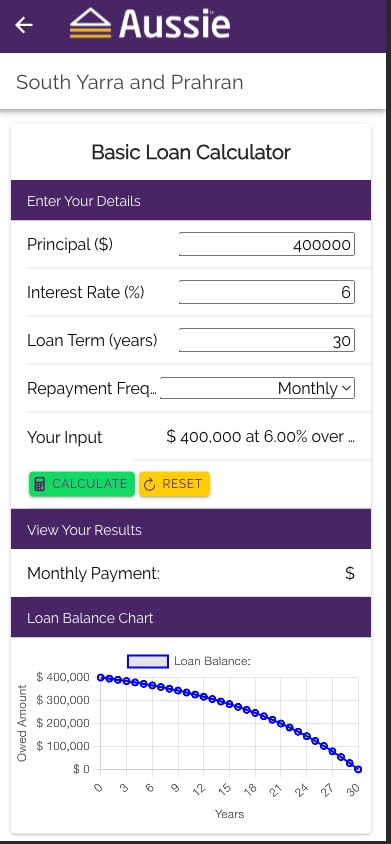
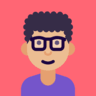
+2
Sharing
References
Technology refinement and experience sharing
1. Componentization
2. JavaScript asynchronous barrier
- Understand asynchronous blocking through (async/await)
async function abc() { for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) { await //expression1 } // expression2 }- In above example, expression2 will execute after for loop
3. Life cycle of Vue
- The life cycle of Vue is actually the whole process from the creation and operation of Vue instances to destruction. We can run our own code at a specific stage of the process. The following are the main stages of this life cycle:
- beforeCreate
- After the instance is initialized, it is called before data observer and event/watcher event configuration.
- created (!)
- After the instance has been created, it is called to complete the data observation, the operation of attributes and methods, and the watch/event event callback. However, the mount phase has not yet started, and the $el attribute is currently invisible.
- beforeMount
- It is called before the mount starts, and the relevant render function is called for the first time. This is the stage to start rendering virtual DOM.
- mounted (!)
- The instance is mounted on the DOM and called. At this stage, you will see that this.$el has replaced the original content.
- beforeUpdate
- When the data is updated, it is called before the virtual DOM is re-rendered and patched. You can change the state further in this hook, which will not trigger an additional re-rendering process.
- updated (!)
- The virtual DOM is re-rendered and patched due to data changes, after which the hook will be called. When this hook is called, the component DOM has been updated, so you can now perform operations that rely on the DOM.
- beforeDestroy
- Called before the instance is destroyed. In this step, the instance is still fully available, which means that we can use this life cycle to complete any type of cleaning work, such as clearing the timer or destroying the DOM elements we added manually.
- destroyed
- Vue instance is called after it is destroyed. After the call, everything indicated by the Vue instance will be unbound, all event listeners will be removed, and all subinstances will be destroyed.
4. JavaScript array functions
1. map()
- return an new array
2. reduce()
- accumulator
- currentValue
- currentValueIndex (optional)
// Example of Reconstructuring data structure let colorCount = items.reduce((total, item) => { // If the color is already in the accumulator object, increase the number of colors. // If the color is not yet in the accumulator object, create a new key and set the number. total[item.color] = (total[item.color] || 0) + item.amount return total }, {})
3. find()
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44] const found = array1.find((element) => element > 10) console.log(found) // Expected output: 12
4. findIndex()
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44] const isLargeNumber = (element) => element > 13 console.log(array1.findIndex(isLargeNumber)) // Expected output: 3
5. filter()
- return an new array
const words = ['spray', 'limit', 'elite', 'exuberant', 'destruction', 'present'] const result = words.filter((word) => word.length > 6) console.log(result) // Expected output: Array ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"]
6. concat()
const words = ['spray', 'limit', 'elite', 'exuberant', 'destruction', 'present'] const result = words.filter((word) => word.length > 6) console.log(result) // Expected output: Array ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"]
7. slice()
- The original array will not be modified.
const animals = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'elephant'] console.log(animals.slice(2)) // Expected output: Array ["camel", "duck", "elephant"] console.log(animals.slice(2, 4)) // Expected output: Array ["camel", "duck"] console.log(animals.slice(1, 5)) // Expected output: Array ["bison", "camel", "duck", "elephant"] console.log(animals.slice(-2)) // Expected output: Array ["duck", "elephant"]
8. splice()
- will change original array
- To create a new array with a segment removed and/or replaced without mutating the original array, use toSpliced(). To access part of an array without modifying it, see slice().
- 0 insert
- 1 replace
const months = ['Jan', 'March', 'April', 'June'] months.splice(1, 0, 'Feb') // Inserts at index 1 console.log(months) // Expected output: Array ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "June"] months.splice(4, 1, 'May') // Replaces 1 element at index 4 console.log(months) // Expected output: Array ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "May"] months.splice(1, 1) // Remove 1 element in index1 console.log(months) // Expected output: Array ["Jan", "March", "April", "May"]
5. Firebase querySnapshot
access data quickly
window.axip.firestore .collection(path) .get() .then((querySnapshot) => { const transformedData = querySnapshot.docs.map((doc) => { const data = doc.data() return { id: doc.id, name: data.name, } }) }) // for Vue Optional API store transformed data this.fetchedData = transformedDataDynamically bind class in Vue
:class="{'class-name': [condition]}"[condition]refers to Ternary expression
6. Vue -> Search Page Component
- Reconstructuring data
- Define searchQueryItem variable
- Use v-model in template to fulfil 2-way binding of searchQueryItem
- Utilize watch to supervise searchQueryItem change
- Then dynamically pass new data structure to the sub components
- 3 levels new constructed data structure search watch
watch: { searchQueryItem(newValue) { const keyword = newValue.trim(); // if no keyword if(!keyword) { let myObj = this.deepClone(this.choosedItem[0]); delete myObj['id'] this.searchResults2 = [myObj, new Array(Object.keys(myObj).length).fill(false)]; return; } // get all props const props = Object.keys(this.choosedItem[0]).slice(1); // whether expand or not : boolean list (not includes id) this.whetherExpand = []; const filteredResult = {}; props.forEach((prop) => { const subprops = Object.keys(this.choosedItem[0][prop]) const filteredObj = {}; let countComparedLength = 0; subprops.forEach((subprop) => { let subpropvalue = this.choosedItem[0][prop][subprop]; if(!subpropvalue){ subpropvalue = ""; } if(subpropvalue.includes(keyword) && !subprop.includes(keyword)){ // 3 includes but 2 ! includes filteredObj[subprop] = this.highlightMatch(subpropvalue, keyword); }else if(subpropvalue.includes(keyword) && subprop.includes(keyword)) { // 3 includes and 2 includes filteredObj[this.highlightMatch(subprop, keyword)] = this.highlightMatch(subpropvalue, keyword); }else if(!subpropvalue.includes(keyword) && subprop.includes(keyword)) { // 3 ! includes but 2 includes filteredObj[this.highlightMatch(subprop, keyword)] = subpropvalue; }else { // 3 and 2 ! includes countComparedLength ++; filteredObj[subprop] = subpropvalue; } }) if (countComparedLength === subprops.length ) { if(prop.includes(keyword)){ filteredResult[this.highlightMatch(prop, keyword)] = filteredObj; // 1 includes but 2 and 3 not includes this.whetherExpand.push(false); } } else{ if(prop.includes(keyword)){ // 2 or 3 includes and 1 includes filteredResult[this.highlightMatch(prop, keyword)] = filteredObj; this.whetherExpand.push(true); }else { // 2 or 3 includes and 1 ! includes filteredResult[prop] = filteredObj; this.whetherExpand.push(true); } } }) // store filtered results this.searchResults2 = [filteredResult, this.whetherExpand]; } }
Hi there! Want to support my work?